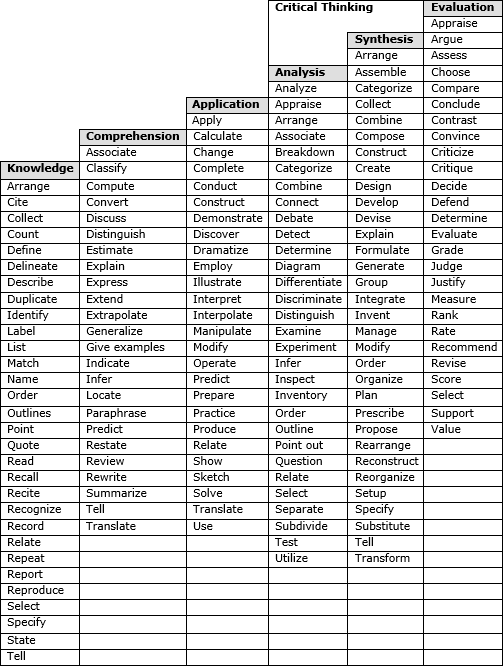
Bloom’s Taxonomy of Action Verbs
In 1956, Benjamin Bloom first described a hierarchy of cognitive skills, with higher-level skills building upon those at lower levels. His hierarchy, and verbs associated with these various levels, have been extensively discussed, revised, and enlarged. The following is a short description of each cognitive skill.
Knowledge: Standards that ask the learner to recognize and recall facts and specifics; rote memorization
- Observation of information, memorizing
- Recognizing, recalling, identifying
- Knowledge of major ideas
- Mastery of subject matter
Comprehension: Standards that ask the learner to interpret, summarize, or paraphrase important information
- Understanding information
- Translating from one medium or context to another
- Interpreting facts
- Organization and selection of facts and ideas
- Describing in one’s own words
- Predict consequences
Application: Standards that ask the learner to use concepts in a situation different from the original learning context
- Use methods, concepts, theories in new situations
- Use of information, facts, rules and principles
- Solve problems using required skills or knowledge
- Applying information to produce some result
Analysis: Standards that ask the learner to separate the whole into its parts, differentiate between parts, and better understand the organization of the whole and the relationship between the parts
- Separation of a whole into component parts
- Finding the underlying structure of a message
- Seeing patterns
- Organization of parts
- Recognition of levels of meaning
- Identification of components
- Identifying motives
Synthesis: Standards that ask the learner to combine learned elements to form a new entity
- Use old ideas to create new ones
- Generalize from given facts
- Relate knowledge from several areas
- Predict, draw conclusions
Evaluation: Standards that ask the learner to make decisions, judge, or select based on criteria and rationale; look at others’ ideas or principles and see the worth of the work and the value of the methods and conclusions
- Compare and discriminate between ideas
- Assess value of theories, presentations
- Make choices based on reasoned argument
- Verify value of evidence
- Recognize subjectivity
- Resolve controversies
- Development of opinions, judgments, or decisions
Bloom’s Taxonomy of Cognitive Skills with Action Verbs List
A relatively new version of Bloom’s Taxonomy is also available from Oregon State University that emphasizes how artificial intelligence may figure into all of this, highlighting the capabilities of AI compared to (still) distinctively human skills.
As noted by Dr. Gavin Henning, a leading proponent of equitable assessment, there are still other approaches to categorizing learning outcomes:
View additional resources collected by Dr. Henning.
Back to Top
